What is E-Waste?
E-waste is short for electronic waste. This include discarded products such as computers, televisions, smartphones, tablets, and printers.
E-Waste differs from regular waste in one major way. Many of the electronics you throw away contain lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants. Not only are these materials toxic, but they’re also considered bio-accumulative. This means they concentrate in the human body, causing negative impacts on fetal development and nursing infants.
Fast Facts
- The United States generated 6.92 million tons of e-waste, about 46 pounds per person, in 2019. It recycled only 15% of the material.
- Recycling 1 million laptops saves the energy equivalent to the electricity used by 3,657 U.S. homes in a year, according to the EPA.
- For every million cell phones that are recycled, 35,274 pounds of copper, 772 pounds of silver, 75 pounds of gold, and 33 pounds of palladium can be recovered, according to the EPA. For those not familiar with palladium, it’s a precious metal using for making electrical contacts as well as surgical instruments and parts for watches.
- It takes 500 pounds of fossil fuel, 50 pounds of chemicals, and 1.5 tons of water to manufacture one computer and monitor, according to the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
- Not all e-waste recyclers are the same. There are safer ways to recycle e-waste, and then there are companies that simply export the waste to developing countries. Rather than monitoring the recycling of e-waste for health and human safety standards in these developing countries, many businesses simply have residents disassemble the electronics for scrap metal, exposing the workers to toxic materials. Look for an e-waste recycling company that has been vetted through e-stewards.org.
- Americans throw out approximately 416,000 mobile phones each day, according to 2014 figures from the EPA. That equates to more than 151 million phones thrown away in one year.
- The United Nations estimates that global e-waste volumes could increase by as much as 39% to 74.7 million tons a year by 2030.
Benefits Of Recycling
Recycling down to raw materials from end-of-life electronics is the most effective solution to the growing e-waste problem. Most electronic devices contain a variety of materials, including metals, plastics and other materials that can be recovered for future uses. By dismantling and providing reuse possibilities, intact natural resources are conserved and air and water pollution caused by hazardous disposal is avoided. Additionally, recycling reduces the amount of greenhouse gas emissions caused by the manufacturing of new products. It simply makes good sense and is efficient to recycle and to do our part to keep the environment green.

IT ASSET DISPOSITION
What is ITAD? ITAD stands for IT Asset Disposition, which provides clients with solutions to handle redundant IT assets and computer equipment through secure data destruction services such as hard drive shredding, degaussing, and disintegration.
When you recycle your electronics with Digital Solutions, you can be sure all data on all of your devices will be thoroughly sanitized beyond recovery using the standards set out by the Department of Defense, and superseded by National Institute for Standards and Technology NIST 800-88 Clear and NIST 800-88 Purge.
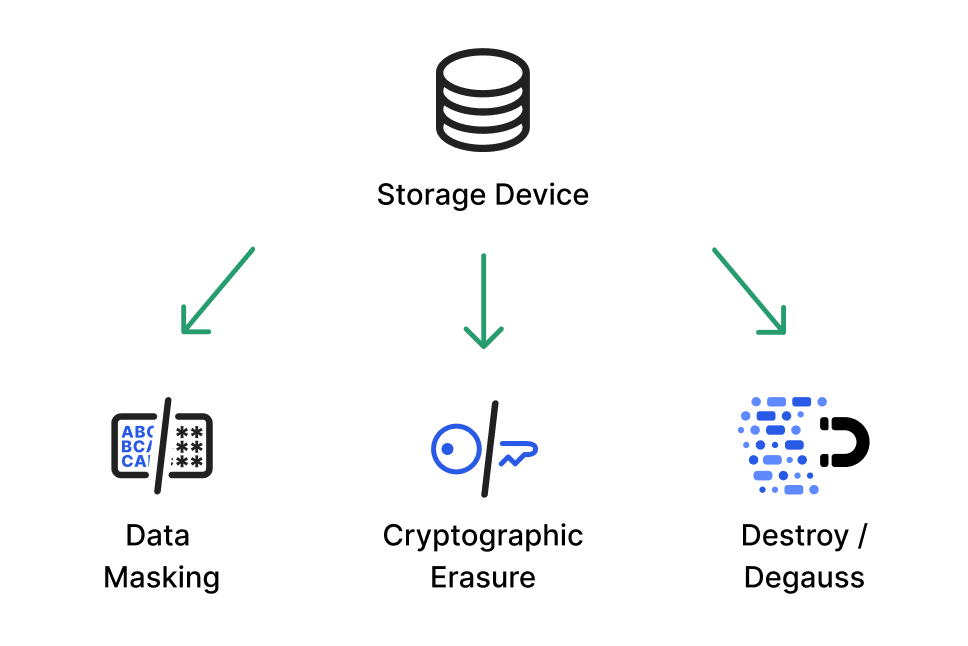
Data Sanitation Methods
Data Destruction: The most obvious way to sanitize a device is to physically destroy the storage media or the device it is a part of—for example, destroying a hard disk or an old laptop with an embedded hard disk.
Data Erasure: This technique uses software to write random 0s and 1s on every sector of the storage equipment, ensuring no previous data is retained.
This is a very reliable form of sanitization because it validates that 100% of the data was replaced, at the byte level.
Cryptographic Erasure: This method uses public-key cryptography, with at least 256 bits, to encrypt the entire drive. The key is discarded and data becomes unrecoverable. Encryption is a fast and effective way to sanitize storage devices. It is best suited for removable or mobile storage devices, or those that contain highly sensitive information.
Data Masking: Masking involves creating fake versions of the data, which retain structural properties of the original data (for example, replacing real customer names with other, randomly-selected names). Data masking is highly effective for sanitization. Effectively, it sanitizes data on the device while it is still in use.
Types of Equipment accepted for recycling
- Computers (laptop and desktop)
- Monitors
- Keyboards and Mice
- Printers/Scanners
- Fax/Copy
- Servers (blade or tower)
- Networking Equipment
- Cell Phones
- Communication Equipment
- Misc. Electronics
If you have e-waste that you would like to recycle, fill out the form below with your preference of dropping off, or having it picked up. Both free of charge.